Xie Zhiguo Wu Changshun
China Quality Certification Center, Shanghai Lanhui Testing Technology Co., Ltd.
Abstract: With the large-scale promotion and application of flame-retardant cloth wire products, the industry is increasingly concerned about how to understand and use the requirements of bundled flame retardant in the field of cloth wire products. This article has passed standard interpretation and carried out verification tests to focus on bundled wire products. The scope of application, classification and arrangement of coverage and other hot spots shared relevant standard understanding, test data and opinions and suggestions.
Keywords: cloth wire, bundled flame retardant, verification test
In recent years, various construction projects have paid increasing attention to the flame-retardant performance of single-core non-sheathed cloth wires (hereinafter referred to as "cloth wires"), as well as the maturity of domestic related manufacturing processes, the improvement of raw material performance and the standard of flame-retardant wires. Implementation, bundled flame-retardant cloth wire products have been widely promoted and applied, occupying an important share of the cloth wire market.
At present, the flame-retardant characteristics of bundled flame-retardant cloth wires are based on the series of standards GB/T 19666 "General Rules for Flame-retardant and Fire-Resistant Wires, Cables or Optical Cables" and GB/T 18380 "Combustion Tests of Cables and Optical Cables under Flame Conditions". Add the bundle flame retardant test category (ZA, ZB, ZC, ZD) to the product model for identification. In the current situation, on the one hand, due to the habit of full coverage of models in the cable industry, all bundled flame retardant categories (ZA, ZB, ZC, ZD) are applied to full specifications of cloth wire products indiscriminately, such as Z(A, B, C, D)-BV 450/750V 1.5~400. On the other hand, due to the ranking of ABCD in common sense and the ranking of non-metal content in the test from high to low, a large number of manufacturers, users and technical institutions in the industry have flame retardant Class A performance superior to (covering) Class B, C The order of class and then to class D is understood and put into actual quality control.
However, with the large number of applications of bundled flame-retardant cloth wire products and the continuous accumulation of related flame-retardant test data, the industry has raised questions about the scope of application, classification and arrangement of different bundled flame-retardant categories in cloth wire products. Questions and thinking are increasing day by day. In order to promote the relevant parties to more accurately understand the relevant application requirements of the bundled flame-retardant category in the field of wired wires, and guide the development, production and quality control of related products, this article will pass standard interpretation and verification test analysis, focusing on the bundled flame-retardant cloth wires Concerned about the related questions to answer and give suggestions.
The GB/T 18380.33~36-2008 standard summarizes the requirements of each flame retardant category as follows:
1、Scope of application
2、Test conditions and qualification
The test conditions are different for different types of parts, such as fire time, sample arrangement, etc., but in the qualification judgment, all types are: the carbonization range on the sample should not exceed 2.5 m above the bottom edge of the torch.
The specific parameters are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Different types of bundled flame retardant test requirements
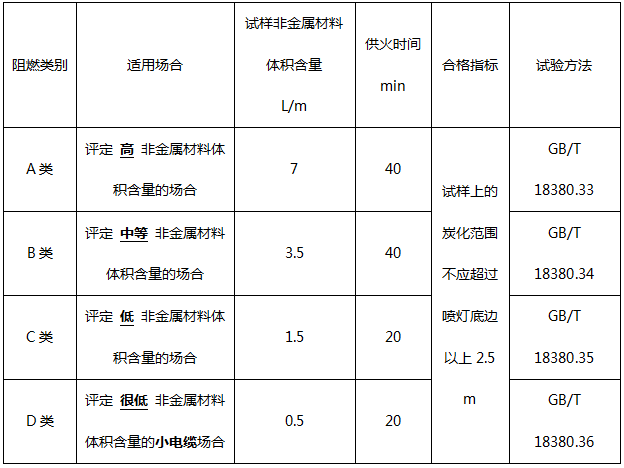
The above comparison shows that the relevant standards for bundled flame retardant do not give the definition of the level, but use the category as the code, such as category A, B, C and D, and there is no clear or implied test of different categories. The high and low levels of the product's flame retardant performance assessment only indicate that it is suitable for the occasions of different non-metallic material volume content.
summary:
According to standard analysis, it can be seen that the bundled flame-retardant (ZA, ZB, ZC, ZD) categories, the main difference lies in the application of different assessment occasions, not the level of flame retardant performance or grades, which does not exist in the standard setting High and low level relationship.
In the wire and cable bundled flame retardant test standard GB/T 18380.33~36, except for the flame retardant class D, it is clearly stated that it is applicable to "small cables with an outer diameter not exceeding 12 mm and a cross section not exceeding 35 mm2" (refer to GB/T The original text of the IEC 60332-3-25:2018 standard corresponding to 18380.36 has been partially adjusted. The original text of IEC 60332-3-25 is "This document relates only to small cables of overall diameter 12 mm or smaller and cross-section of 35 mm2 or smaller installed on the test ladder to achieve a nominal total volume of non-metallic material of 0.5 L/m of test sample.”), the others have not given clear restrictions on wire and cable products in the scope of application. At the same time, the widely adopted GB/T 19666 standard general rule does not give detailed definitions on the application of different flame retardant categories in cloth wire products. Therefore, there are a large number of flame retardant cloth wire products of ZA~ZD fully flame retardant on the market. , Such as Z(A,B,C,D)-BV 450/750V, WDZ(A,B,C,D)-BYJ 450/750V, etc.
However, the restrictions imposed by the installation conditions of the samples in the standards of GB/T 18380.33~35 (flame retardant Class A, Class B, Class C) on the wiring products should be concerned.
In the installation of flame-retardant A, B and C samples, it is clearly required: “For cables with at least one conductor with a cross-section of more than 35 mm2, each cable sample section shall be fixed on each horizontal steel ladder with a metal wire. The cable sample section should be installed in front of the steel ladder in a single layer, and the interval between the cable sample sections should be 0.5 times the cable diameter, but not more than 20 mm. No matter whether the standard steel ladder or the wide steel ladder is used, the edge of the sample The minimum distance from the vertical surface inside the steel ladder shall be 50 mm. The maximum width of the specimen on the standard steel ladder shall be 300 mm, and the maximum width of the specimen on the wide steel ladder (only for category A) shall be 600 mm".
According to the conventional structure of cloth wire products and the volume requirements of non-metallic materials in different flame retardant tests, the number of samples of cloth wires with a nominal conductor cross-section greater than 35 mm2 in the flame retardant A, B and C tests can be roughly calculated as Table 2 shows. The comparison shows that for the cloth wires with a nominal conductor cross-section greater than 35 mm2, according to the above-mentioned analysis of the interval arrangement and the number of installation requirements, the flame-retardant A and B wires have no corresponding specifications to meet the test sample installation requirements. Only part of the large specifications can meet the C type.
Table 2 Installation of flame-retardant test samples for cloth wire products with conductors with a nominal cross-section of 35 mm2 or more
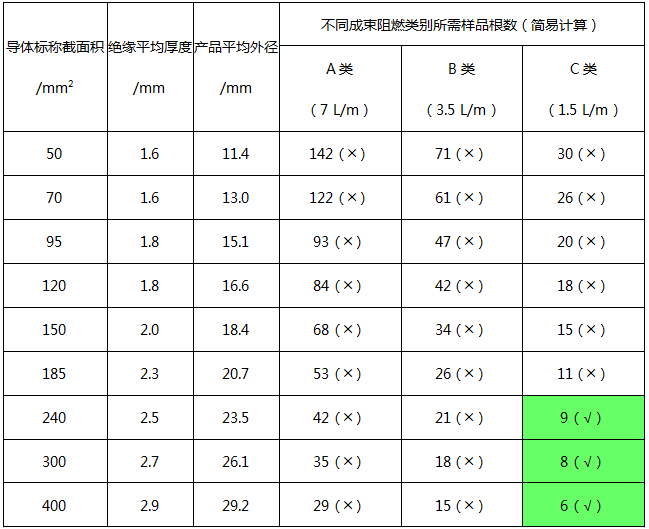
Note:
1. Due to the limitation of the width of the steel ladder, the symbol (╳) means that the sample cannot be installed for testing, and (symbol √) means that the sample can be installed for testing.
2. The cloth wires referred to in this article generally refer to single-core non-sheathed wires with a rated voltage of 450/750V and below and a maximum specification of 400 mm2 of conductor nominal cross-section.
3. The value of the average insulation thickness refers to the specified value of insulation thickness in GB/T 5023.3 (additional 0.2~0.3mm); the formula for calculating the average outer diameter: average outer diameter = conductor outer diameter + 2X average insulation thickness, where the conductor outer diameter Refer to the nominal calculated value of the conductor outer diameter of the stranded conductor (type 2) in IEC60719.
In addition, GB/T 18380.36 clearly states that the flame-retardant Class D is suitable for "small cables with an outer diameter not exceeding 12 mm and a cross section not exceeding 35 mm2". Coincidentally, as a typical single-core non-sheathed cable product, GB/ Type BV and RV in the T 5023.3 standard, and BYJ and RYJ in the JB/T 10491 standard, the upper limits of the average outer diameter of the 35 mm2 wire are 10.9 mm and 11.7 mm, respectively. This data is consistent with the flame-retardant Class D limit conditions (Nominal cross-section of conductor 35 mm2 and below and outer diameter of 12 mm and below) are consistent, and it also reflects that the most direct match is flame-retardant class D for wired wire products with a nominal conductor cross-section of 35 mm2 and below. This point can also be found in other product standards. For example, the low-smoke, halogen-free, flame-retardant cable structure specified in GB/T 12528-2008 "Cables for Rail Transit Vehicles with AC Rated Voltage 3kV and Below" is a typical single-core In the non-sheathed wire structure, in the standard 7.4.8 Bundled Cable Burning Test Clause, the Bundled Burning Test of the standard low-smoke halogen-free cables is limited to the flame-retardant C and D cables with an outer diameter greater than 12 mm It is required to pass the C category, and the requirements of no more than 12 mm pass the D category.
summary:
According to the analysis of relevant standards, we can see:1) The cloth wire with a nominal cross section exceeding 35mm2 neither meets the sample installation requirements of the bundled flame-retardant type A and B test, nor does it meet the applicable scope of the flame-retardant type D test. Only some specifications can be applied to flame-retardant Type C test.
2) The cloth wires with a nominal cross section of 35mm2 and below can be applied to bundles of flame-retardant A, B, C, and D types due to no restrictions in the standard, but from the description of the scope of GB/T 18380.36, the most directly matched It is flame retardant Class D。
4. Suggestions for the Bundle Burning Test of Flame Retardant Fabric Wire Products
For flame-retardant cloth wire products, how to choose the bundle burning test method is one of the focuses of the industry.
First of all, for flame-retardant cloth wire products with a nominal conductor cross-section of more than 35 mm2, since it neither meets the applicable scope of flame-retardant D category nor meets the installation requirements of flame-retardant A and B test samples, the cloth wires within this range For the flame retardant test, only the flame retardant C type test specified in GB/T 18380.35 should be selected.
For flame-retardant cloth wire products with a nominal conductor cross-section of 35 mm2 and below, although in principle, it can be applied to the test of flame-retardant A to D, but if each flame-retardant category is selected for testing, it will face a sharp increase Therefore, in actual quality control activities such as sampling inspection, certification or evaluation, the coverage principle is usually used to select representative samples for a certain flame-retardant test. The priority of the flame-retardant test category is usually It is Class A-Class B-Class C-Class D. However, it is questioned whether this sorting is the best solution for wiring products, especially the wiring products in the category of small cables whose nominal conductor cross-section does not exceed 35 mm2 and the outer diameter does not exceed 12 mm.
In order to verify the relevant data and obtain guidance, the China Quality Certification Center (CQC) and Shanghai Lanhui Testing Technology Co., Ltd. (ISTCW) organized 8 mainstream cloth wire manufacturers in the United Nations to organize and carry out the flame retardant verification test of the cloth wires. In the verification test, two representative insulation materials of typical home improvement wire specifications were selected as the verification samples, involving 5 sets of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulated ZA-BV 450/750V 2.5 wires and 5 sets of cross-linking Polyolefin (XLPO) insulated WDZA-BYJ 450/750V 2.5 wire. Cable manufacturers strictly follow the wire structure requirements specified in the verification test plan, uniformly prepare verification samples that meet the standard requirements, and then verify the samples strictly follow the GB/T 18380.33~36-2008 standard requirements, and adopt relatively uniform sample installation and test operation requirements , In the same test equipment, 10 groups of verification samples were concentrated on the bundled flame retardant Class A, B, C and D combustion tests (a total of 40 batches of tests), and the vertical flame spread after the test was measured distance.
Taking into account the determination of different types of flame retardant tests: the carbonization range on the sample should not exceed 2.5 m above the bottom edge of the torch. According to the inertial understanding, the flame retardant performance of Class A is better than (covered) Class B, Class C to Class D, which means that the stringency of the bundled flame retardant test is ranked as A>B>C>D, then It can be inferred that after the same sample is subjected to the test of different flame retardant categories, the carbonization height index reflecting the flame extension should show the law of A>B>C>D.
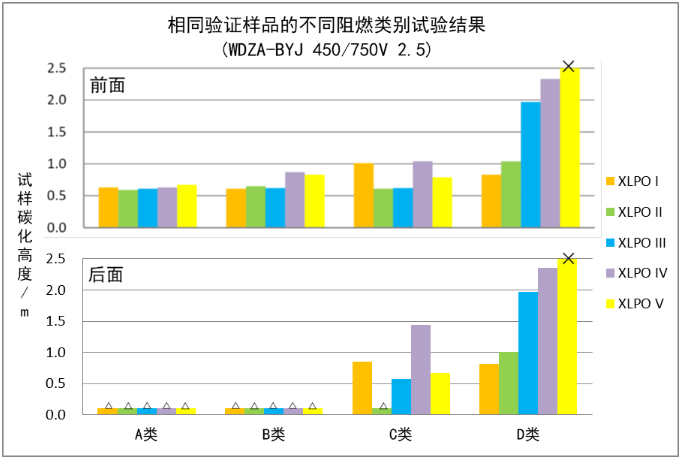
Figure 1 Validation test results of sample WDZA-BYJ 450/750V 2.5
(a: The above table is the carbonization height in front of the steel ladder, and the following table is the carbonization height behind the steel ladder; b: "△" represents no carbonization; c: "X "It means that the carbonization height exceeds the requirement and is unqualified.)
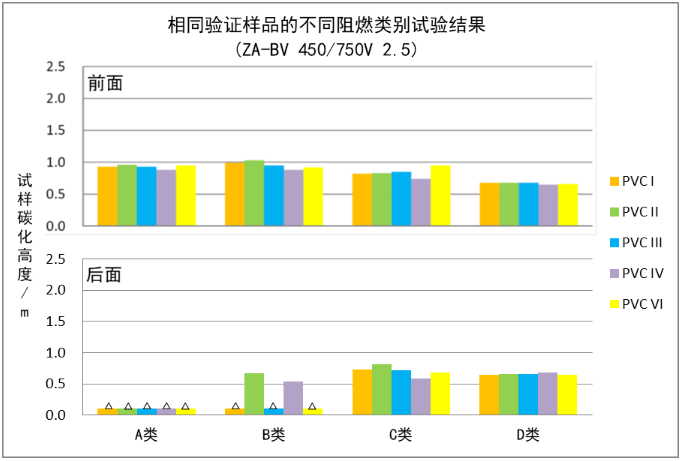
Figure 2 Verification test results of sample ZA-BV 450/750V 2.5
(A: The above table is the carbonization height in front of the steel ladder, and the table below is the carbonization height behind the steel ladder; b: "△" represents no carbonization.)
However, through comparison and analysis to verify the test data, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, whether it is PVC insulated ZA-BV 450/750V or XLPO insulated WDZA-BYJ 450/750V wire, the resistance of the same verification sample The carbonization heights under the combustion tests of A, B, C and D did not show an obvious rule of A>B>C>D. On the contrary, the BYJ type samples basically showed the law of carbonization height D>C>B>A, and even the flame retardant A and B tests passed but the flame retardant D test failed. There is no significant difference in the carbonization height of the BV type samples in the flame retardant A, B, C and D tests. Moreover, regardless of the BYJ or BV type samples, in all the flame retardant type A tests and most of the flame retardant type B tests, the samples behind the steel ladder were not carbonized. In comparison, the steel after the flame retardant type D test The samples behind the ladder were all carbonized.
For this kind of upside-down phenomenon, through experimental observation, it is speculated that it may be due to the close arrangement of small cross-section wires in the flame-retardant A and B tests, which makes it difficult for the flame to spray or spread to the inside of the sample, and it is difficult for air to enter the test in large quantities. Kind of internal. This conjecture can also be observed from the installation drawings of samples of different flame-retardant categories of cloth wires. According to the requirements of the volume content of non-metallic materials under different bundled flame-retardant categories, the 2.5mm2 specification cloth wires are in the flame-retardant Class A test. The average number is about 1,000, and about 500 for class B. It can be seen from Figure 3 that the flame retardant class A and class B samples have formed a very compact structure after installation, which may inhibit the penetration and spread of flame, resulting in burning The flame spread and carbonization distance in the test is shorter than the flame retardant C and D.

Figure 3 Samples of typical ZA-BYJ 450/750V 2.5 samples after bundled flame retardant A~D test (including the number of installed elements and the carbonization height in front of the steel ladder)
summary:
Through the batch verification test, it can be seen that for typical small cross-section flame-retardant cloth wire products with a nominal conductor cross-section of 35 mm2 and below, if viewed from the perspective of the carbonization height after the combustion test, the reference order of the severity of the different flame-retardant category tests is recommended as : D>C>B>A.
At the same time, the flame retardant Class A and Class B tests in this verification test are calculated according to the standard requirements. The number of test samples required is about 1000 and 500 respectively. The tightness of the sample installation in the actual test is shown in Figure 3. This kind of high-density and large-volume installation and laying of bundles has largely deviated from the mainstream application scenarios of actual wiring products, and the relevant reference value of the test results is limited.
Furthermore, for flame-retardant cloth wire products with a nominal conductor cross-section of 35 mm2 and below, when considering relevant resource constraints and program optimization, if the coverage priority principle is required, it is recommended to give priority to the actual installation scenarios. Flame retardant class D or C is tested, covering flame retardant class A and B.
With the increasing attention to the flame-retardant performance of wires and cables in China, a large number of wire and cable bundle burning tests have been widely used, and relevant parties are paying more and more attention to the accuracy of test results. However, the continuous expansion of laboratories is in the standard The understanding of specific requirements and some differences in the implementation of actual operations pose risks and challenges to the validity of the results of partial beam flame retardant tests. In order to promote the laboratory to more comprehensively grasp the relevant points of the flame retardant of wire and cable bundles, this chapter shares the key points of concern and operation suggestions for specific test references.
a) When some testing institutions have many combustion tasks, after the combustion test of the previous sample is completed, the combustion test of the second sample is often started before the temperature of the cabinet has dropped to the ambient temperature, which will seriously affect the second sample. The test results of a single sample;
b) For multiple cable samples, especially small outer diameter samples, they should be kept vertical after being tied to the ladder frame. If there is an excessive gap between the single samples due to bending, it will affect The test results are so serious that there is a difference between qualified and unqualified;
c) The air intake method, air intake and stability during combustion must meet the standard requirements. In addition, the old-fashioned airtight extraction and exhaust methods on the top of the box will have an impact on the test results;
d) The use of mass flow meters is more conducive to the control of combustion gas and air flow;
e) The combustion surface of the burner to the sample on the ladder frame The distance of the surface will affect the test results;
f) Burning torches are consumables, and the vents on the combustion surface of the torches need to be cleaned frequently, and the torches should be replaced if necessary.
Flame retardant performance is an important safety item for wire and cable products. Especially in the field of construction wires, bundled flame retardant wire products have been widely promoted. At present, in the face of the trend of non-standard application of flame-retardant category and even "abuse" of cloth wire products, relevant parties, including manufacturers, marketing companies, design units, user units and technical institutions, combine the actual characteristics and laying of the products. In the scene, it is particularly important to accurately understand the relevant requirements for the bundled flame retardant of cloth wire products. In this article, based on standard analysis and verification tests, the author summarized and refined the following points:
1) Bundle flame retardant (ZA, ZB, ZC, ZD) categories, the main difference lies in the different applicable evaluation occasions, not the classification of flame retardant performance. In theory, there is no relationship between high and low levels.
2) For flame-retardant cloth wire products with conductors with a nominal cross-section greater than 35 mm2, neither meets the installation requirements of flame-retardant A and B test samples, nor does it comply with the scope of flame-retardant D, only some specifications can meet flame-retardant C Installation requirements for test samples.
3) For flame-retardant cloth wire products with a nominal conductor cross-section of no more than 35 mm2, the verification test of multi-bundle burning category A~D shows that whether it is a PVC insulated cable or a cross-linked polyolefin insulated cable, the typical small The analysis of the carbonization height of the samples in the different flame-retardant category tests shows that the flame-retardant type D or C type test is more stringent and representative than the flame-retardant type A and B for such small cross-section cables. . That is to say, using the flame-retardant Class A or Class B method to evaluate the home improvement wires with a small number of laying installations is risky. This also brings a hint to the cable process design, that is, the oxygen index of the insulation design of the flame-retardant D or C cloth wire should be higher.
Therefore, for the bundled flame retardant test of cloth wire products, when considering related resource constraints and program optimization, it is recommended to first combine the actual installation and laying scenes. If there is no specific scene, give priority to flame retardant D or C for testing. It is worth mentioning that with the revision of the GB/T 19666-2019 standard, the China Quality Certification Center has made corresponding measures for the certification scope and sample selection principles in the implementation rules for the certification of flame-retardant cloth wires (CQC11-463401-2020) Optimization adjustments. This article shares the relevant standard understanding, test data and opinions and suggestions around the hot spots of bundled flame retardant of cloth wire products, which will help related parties and user markets to more scientifically and objectively understand the application of bundled flame retardant in cloth wire products. Relevant units to further do the research and development, production, quality improvement and quality control of flame-retardant cloth wire products have important reference value and guiding significance.
Add.:Room703、705/7F, Development Building, Tian An Hi-Teck Ecological Park, No.555 North Road Panyu Avenue, Panyu District, Guangzhou City, 511400, China
Tel.:020-39211670 Fax:020-39211640 E-mail:info@certitek.cn

